Genetic in failure of conception
Genetic infertility refers to difficulties in conceiving or maintaining a pregnancy that arise from underlying genetic causes. These genetic factors may interfere with the production of eggs or sperm, disrupt fertilization, impair embryo development, or increase the risk of miscarriage and congenital conditions. Genetic infertility can affect both women and men, and in some cases, it may involve both partners simultaneously.
Unlike infertility caused by hormonal, anatomical, or lifestyle factors, genetic infertility is rooted in changes within chromosomes or genes. These changes may be inherited from parents, occur spontaneously during early development, or arise due to errors in cell division. Understanding genetic infertility is essential because it not only impacts the chances of pregnancy but can also influence the health of future offspring.
How Genetics Influence Fertility
Human reproduction depends on the precise transmission of genetic material. Each egg and sperm normally carries 23 chromosomes, which combine during fertilization to create an embryo with 46 chromosomes. Any disruption in chromosome number, structure, or gene function can interfere with this process.
Genetic infertility may result from:
- Chromosomal abnormalities (structural or numerical changes)
- Gene mutations that affect reproductive development or function
- Inherited genetic disorders
- Errors in meiosis, the cell division process that produces eggs and sperm
These genetic issues may prevent conception entirely, lead to early pregnancy loss, or cause serious health conditions in the embryo.
Genetic Causes of Infertility in Women
Several genetic conditions can impair ovarian development, egg production, or hormonal regulation in women.
Turner Syndrome
Turner syndrome occurs when a woman is missing all or part of one X chromosome. Women with this condition often have underdeveloped ovaries, leading to primary ovarian insufficiency (POI). As a result, natural conception is usually not possible without medical intervention.
Fragile X Premutation
Women who carry a premutation in the FMR1 gene are at increased risk of developing fragile X–associated primary ovarian insufficiency. This condition can cause reduced ovarian reserve, irregular menstrual cycles, and early menopause, sometimes occurring in the 20s or 30s.
Kallmann Syndrome
Kallmann syndrome is a genetic disorder affecting the production or action of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This disrupts the hormonal signals needed for puberty and ovulation, leading to absent or delayed sexual development and infertility if untreated.
Other Genetic Factors in Female Infertility
Additional genetic variations may affect follicle development, hormone receptors, or egg maturation. In some women, these genetic influences lead to poor egg quality, repeated IVF failure, or recurrent pregnancy loss.
Genetic Causes of Infertility in Men
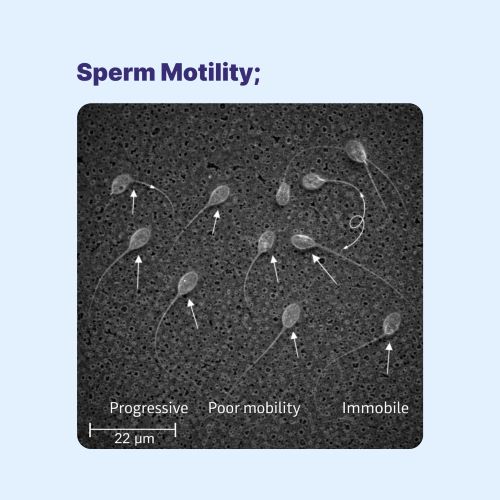
Genetic factors are a significant cause of male infertility, particularly in men with very low sperm counts or no sperm production.
Y Chromosome Microdeletions
The Y chromosome contains genes critical for sperm production. Microdeletions in specific regions of the Y chromosome can result in:
- Azoospermia (complete absence of sperm)
- Oligozoospermia (severely reduced sperm count)
These deletions are among the most common genetic causes of severe male infertility and are often detected through specialized genetic testing.
Gene Mutations Affecting Spermatogenesis
Mutations in genes involved in testicular development and sperm formation, such as NR5A1, can impair hormone production and sperm development. Men with such mutations may have abnormal semen parameters despite normal physical appearance.
Chromosomal Abnormalities in Men
Conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY) can severely affect testosterone production and sperm formation. While some men with chromosomal abnormalities may produce small numbers of sperm, many require assisted reproductive techniques to attempt conception.
Genetic Factors Affecting Both Sexes
Some genetic conditions can affect fertility in both women and men.
Chromosomal Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy refers to having an abnormal number of chromosomes. Embryos with chromosomal aneuploidy often fail to implant or result in early miscarriage. Even when pregnancy progresses, aneuploidy can lead to serious congenital conditions.
Single-Gene Disorders
Inherited single-gene disorders, such as cystic fibrosis or Tay-Sachs disease, may not directly prevent conception but can:
- Affect reproductive organs or function
- Increase the risk of infertility-related complications
- Pose serious health risks to offspring
In some cases, carriers of certain genetic mutations may have normal fertility but choose to undergo genetic screening to prevent passing the condition to their children.
Recurrent Pregnancy Loss and Genetics
Genetic abnormalities are a leading cause of recurrent miscarriage. Many early pregnancy losses occur because the embryo has an abnormal chromosome number or structure incompatible with life. Couples experiencing repeated pregnancy loss are often advised to undergo genetic evaluation to identify potential chromosomal rearrangements or inherited mutations.
The Role of Genetic Testing in Infertility
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in identifying the underlying causes of infertility and guiding treatment decisions. Common genetic tests include:
- Karyotyping to analyze chromosome number and structure
- Y chromosome microdeletion testing in men
- Single-gene mutation screening
- Carrier screening for inherited disorders
The results of genetic testing can help clinicians:
- Explain the cause of infertility
- Estimate the chances of natural conception
- Recommend appropriate fertility treatments
- Assess risks to future pregnancies
Treatment Options for Genetic Infertility
While genetic infertility cannot always be cured, modern reproductive medicine offers several pathways to parenthood.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
Techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) can help overcome certain genetic barriers, especially in cases of severe male factor infertility or ovarian insufficiency.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
PGT allows embryos created through IVF to be screened for chromosomal abnormalities or specific genetic mutations before transfer to the uterus. This can:
- Reduce the risk of miscarriage
- Increase the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy
- Prevent transmission of serious genetic disorders
Use of Donor Eggs or Sperm
In cases where genetic conditions severely affect egg or sperm quality, some couples may consider using donor gametes to achieve pregnancy.
Final Thoughts
Genetic infertility is a complex and emotionally challenging condition that affects many individuals and couples. It can involve chromosomal abnormalities, gene mutations, or inherited disorders that disrupt fertility or pregnancy outcomes. Advances in genetic testing and assisted reproductive technologies have significantly expanded the options available to people facing genetic infertility.
Early diagnosis, personalized counseling, and informed decision-making are essential. With appropriate medical support, many individuals with genetic infertility can still achieve their goal of building a healthy family—whether through advanced fertility treatments, genetic screening, or alternative reproductive pathways.