Lifestyle in failure of conception
Lifestyle is one of the most powerful and modifiable factors influencing fertility in both women and men. Unlike age or genetics, lifestyle choices are areas where individuals have significant control, and even small, consistent changes can positively affect reproductive potential. Nutrition, body weight, physical activity, stress levels, smoking, alcohol use, drug exposure, and environmental factors all interact with hormonal regulation, egg and sperm quality, ovulation, implantation, and pregnancy outcomes.
While some lifestyle habits can reduce the likelihood of conceiving naturally or through assisted reproductive technologies (ART), others can actively improve fertility and overall physical and mental health. Understanding these influences allows individuals and couples to take proactive steps toward optimizing fertility.
The Connection Between Lifestyle and Reproductive Hormones
The reproductive system is tightly regulated by hormones produced by the brain, ovaries, testicles, thyroid, and adrenal glands. Lifestyle factors can disrupt or support this delicate hormonal balance. Poor lifestyle habits may interfere with ovulation, sperm production, and implantation, while healthy habits help maintain stable hormone levels and create a supportive environment for conception and pregnancy.
Nutrition and Fertility
Nutrition plays a foundational role in reproductive health. The body requires adequate energy, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to support egg development, sperm production, and hormonal signaling.
A fertility-supportive diet generally includes:
- A variety of fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants
- Whole grains that support stable blood sugar levels
- Lean proteins such as fish, poultry, eggs, legumes, and nuts
- Healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocados, and fatty fish
- Dairy or fortified alternatives that provide calcium and vitamin D
Poor dietary patterns—particularly those high in refined sugars, trans fats, ultra-processed foods, and excessive caffeine—can contribute to insulin resistance, inflammation, hormonal imbalance, and poor egg or sperm quality. Long-term nutritional deficiencies may also reduce the chances of successful conception and increase pregnancy risks.
Body Weight and Fertility
Maintaining a healthy body weight is crucial for fertility. Both underweight and overweight individuals may experience disruptions in reproductive function.
In women:
- Excess body fat can alter estrogen and insulin levels, leading to irregular ovulation or anovulation
- Being underweight may suppress reproductive hormones and stop ovulation altogether
In men:
- Obesity is associated with lower testosterone levels, reduced sperm count, and poorer sperm quality
- Very low body fat can also negatively affect hormone production and sperm development
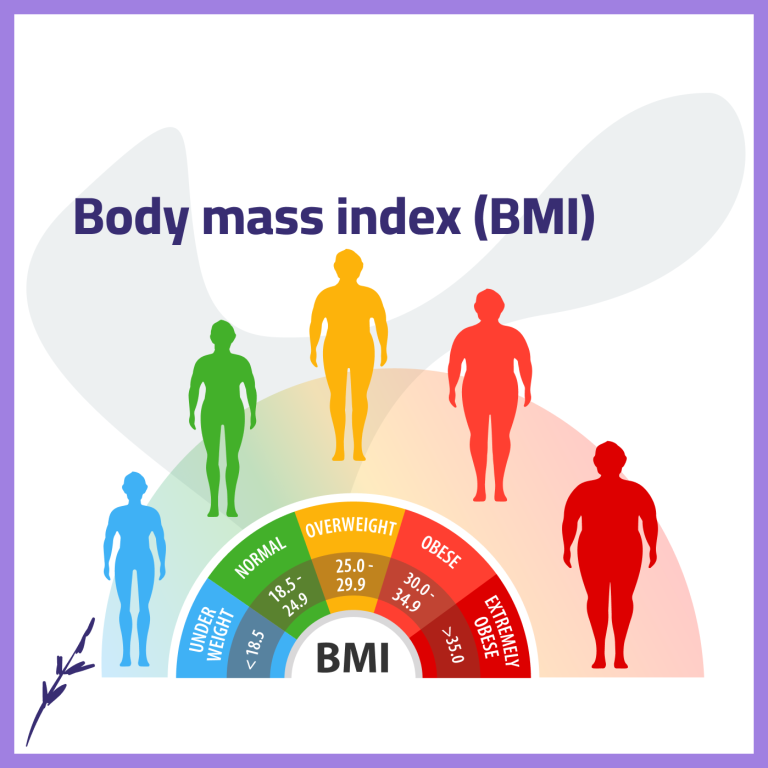
A healthy weight is commonly defined by a body mass index (BMI) between 18.5 and 24.9, though individual body composition and metabolic health are also important considerations. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can improve fertility outcomes and reduce pregnancy complications.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular, moderate exercise supports fertility by improving circulation, reducing stress, supporting metabolic health, and helping regulate hormones. Activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, yoga, and strength training can all be beneficial when performed in moderation.
However, excessive or very intense exercise may negatively affect fertility:
- In women, extreme physical exertion can disrupt ovulation and menstrual cycles
- In men, overtraining may reduce testosterone levels and impair sperm quality
Most fertility specialists recommend moderate exercise for about 30 minutes per day, five days a week, adjusted to individual health and fitness levels.
Stress and Emotional Well-Being
Psychological stress can significantly impact fertility. Chronic stress activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, increasing stress hormones such as cortisol. Elevated stress hormones can interfere with reproductive hormone release, ovulation, sperm production, and libido.
Long-term stress may also:
- Weaken immune function
- Increase inflammation
- Disrupt sleep and appetite
- Reduce sexual desire and intimacy
Managing stress through mindfulness, relaxation techniques, counseling, support groups, adequate sleep, and emotional support can improve both fertility and overall quality of life.
Smoking and Fertility
Smoking is one of the most harmful lifestyle factors for fertility. Tobacco smoke contains numerous toxic substances that directly damage reproductive cells.
In women, smoking can:
- Reduce ovarian reserve
- Damage egg DNA
- Increase the risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy
- Accelerate ovarian aging
In men, smoking can:
- Reduce sperm count and motility
- Increase sperm DNA fragmentation
- Alter hormone levels
Smoking marijuana may also impair sperm quality and disrupt ovulation. Quitting smoking significantly improves reproductive health in both sexes and benefits pregnancy outcomes.
Alcohol and Fertility
Alcohol consumption affects fertility in dose-dependent ways. Even moderate alcohol intake may alter hormone levels and reduce reproductive efficiency.
Alcohol can:
- Disrupt ovulation and menstrual regularity
- Reduce sperm count and quality
- Increase the risk of miscarriage
- Contribute to fetal alcohol spectrum disorders if pregnancy occurs
Limiting or avoiding alcohol when trying to conceive is widely recommended for both women and men.
Drugs and Medications
Illicit drug use has a profound negative impact on fertility. Substances such as cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine, and ecstasy can disrupt hormone production, damage eggs and sperm, and interfere with implantation.
Certain prescription medications—including opioids, some antidepressants, antihistamines, and anabolic steroids—may also affect fertility by altering hormone levels, libido, or sexual function. It is important to consult a healthcare provider before stopping or changing prescribed medications.
Environmental and Occupational Exposures
Environmental factors are increasingly recognized as fertility disruptors. Exposure to toxins such as pesticides, heavy metals, industrial chemicals, radiation, and excessive heat can impair reproductive function.
These exposures may:
- Disrupt endocrine signaling
- Damage egg and sperm DNA
- Reduce sperm production and egg quality
- Increase risks of miscarriage and birth defects
Reducing exposure through protective measures, safe workplace practices, proper ventilation, and informed consumer choices can help protect reproductive health.
Lifestyle Changes and Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
Lifestyle factors not only affect natural fertility but also influence the success of ART procedures such as IVF and IUI. Healthy lifestyle habits can improve egg and sperm quality, embryo development, implantation rates, and pregnancy outcomes, while unhealthy habits may reduce treatment effectiveness.
Final Thoughts
Lifestyle choices are deeply intertwined with fertility. While not all fertility challenges can be resolved through lifestyle changes alone, adopting healthier habits can significantly improve reproductive potential, enhance treatment success, and support long-term health.
By focusing on nutrition, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in moderate exercise, managing stress, avoiding harmful substances, and minimizing environmental risks, individuals and couples can create a more favorable environment for conception and pregnancy. Fertility is not only a medical issue—it is also a reflection of overall physical, emotional, and environmental well-being.